Further Production Enhancements¶
GeoServer Production Settings¶
JVM Settings: Memory And GeoServer Options¶
The .env file provides a way to customize GeoServer JVM Options.
The variable GEOSERVER_JAVA_OPTS allows you to tune-up the GeoServer container and to enable specific GeoServer options.
GEOSERVER_JAVA_OPTS=
-Djava.awt.headless=true -Xms4G -Xmx4G -XX:PerfDataSamplingInterval=500
-XX:SoftRefLRUPolicyMSPerMB=36000 -XX:-UseGCOverheadLimit -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC
-XX:+UseParNewGC -XX:ParallelGCThreads=4 -Dfile.encoding=UTF8 -Djavax.servlet.request.encoding=UTF-8
-Djavax.servlet.response.encoding=UTF-8 -Duser.timezone=GMT
-Dorg.geotools.shapefile.datetime=false -DGS-SHAPEFILE-CHARSET=UTF-8 -DGEOSERVER_CSRF_DISABLED=true -DPRINT_BASE_URL=http://geoserver:8080/geoserver/pdf
-Djava.awt.headless (true)
Work with graphics-based applications in Java without an actual display, keyboard, or mouse A typical use case of UI components running in a headless environment could be an image converter app. Though it needs graphics data for image processing, a display is not really necessary. The app could be run on a server and converted files saved or sent over the network to another machine for display.
-Xms4G -Xmx4G
This means that your JVM will be started with Xms amount of memory and will be able to use a maximum of Xmx amount of memory. Above will start a JVM like with 2 GB of memory and will allow the process to use up to 4 GB of memory. You need to adjust this value depening on your availabnle RAM.
-DGEOSERVER_CSRF_DISABLED (True)
The GeoServer web admin employs a CSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery) protection filter that will block any form submissions that didn’t appear to originate from GeoServer. This can sometimes cause problems for certain proxy configurations. You can disable the CSRF filter by setting the GEOSERVER_CSRF_DISABLED property to true. https://docs.geoserver.org/stable/en/user/security/webadmin/csrf.html
Whenever you need to change one or more of the JVM options, you will need to restart the GeoServer Docker container.
# Hard restart of the container: the only way to update the .env variables
docker-compose up -d geoserver
This command will preserve all the GeoServer configuration and data, since the GEOSERVER_DATA_DIR is stored on a Docker static volume.
Nevertheless, any change you have made manually to the container, e.g. added a new plugin to GeoServer or updated some JARs into the WEB-INF/lib library folder, will be lost.
You will need to add the JARs again and restart GeoServer softly
# Soft restart of the container: the .env variables won't be updated
docker-compose restart geoserver
Global And Services Settings¶
Check the GeoServer Memory usage and status; ensure the
GEOSERVER_DATA_DIRpath points to the static volume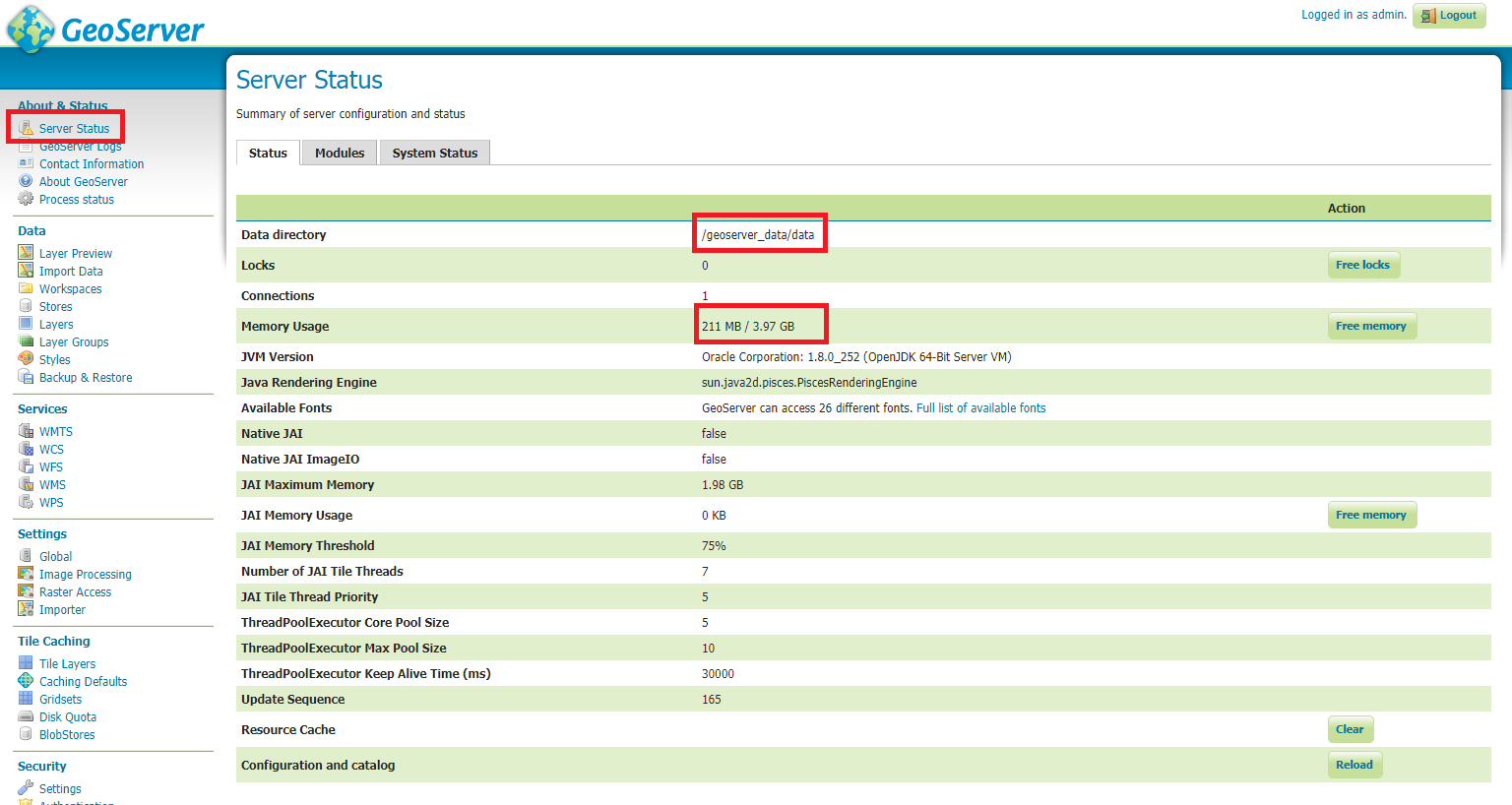
GeoServer Status¶
GeoServer Global Settings; make sure the
Proxy Base Urlpoints to the publlc URL and theLOGGINGlevels are set to Production Mode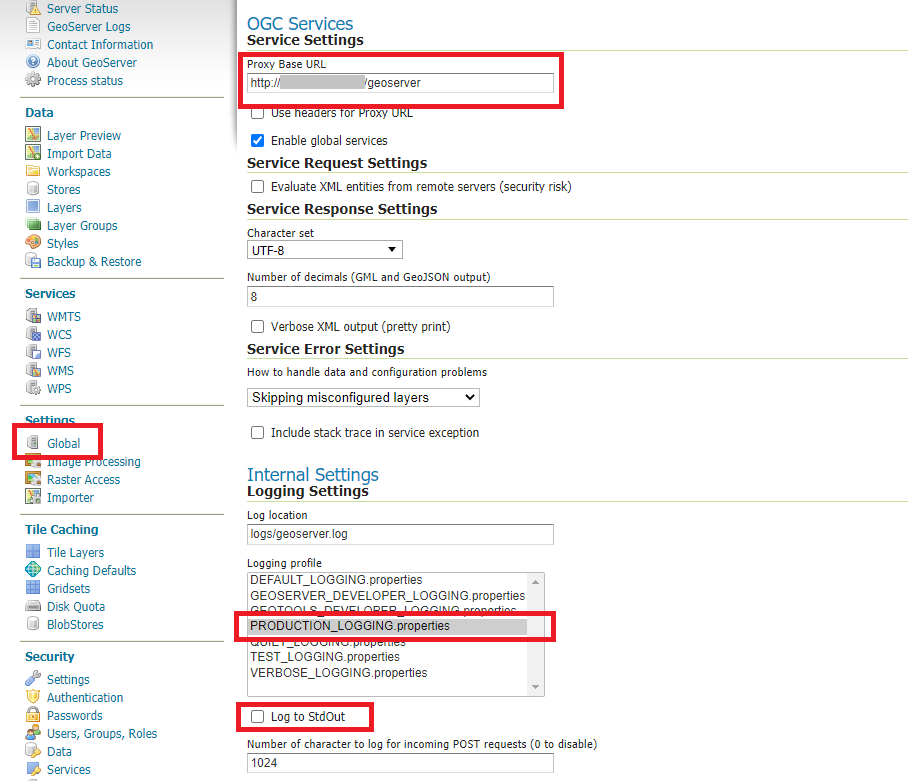
Global Settings¶
GeoServer Image Processing Settings; unless you are using some specific renderer or GeoServer plugin, use the following recommended options
Note
Further details at https://docs.geoserver.org/stable/en/user/configuration/image_processing/index.html#image-processing
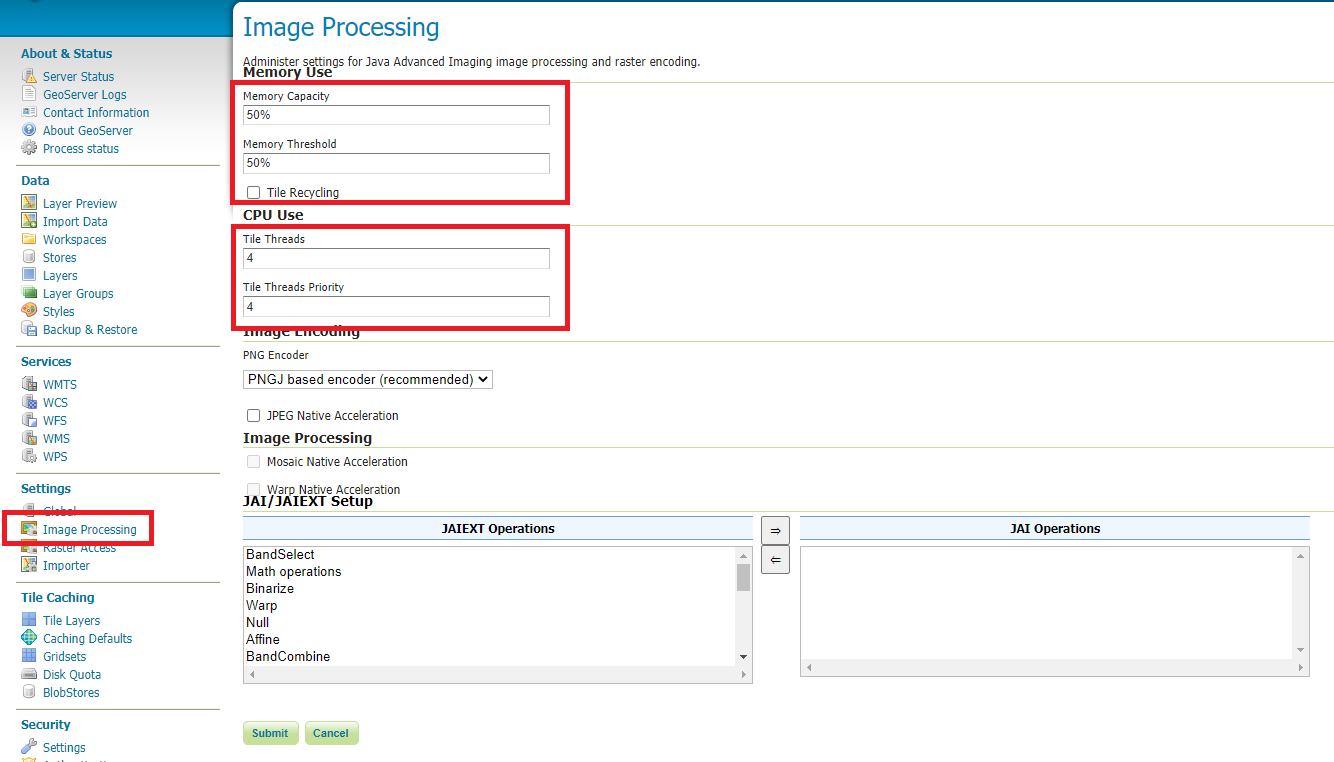
Image Processing Settings¶
Tune up GeoServer Services Configuration; WCS, WFS, WMS and WPS;
WCS: Update the limits accordingly to your needs. Do not use very high values, this will set GeoServer prone to DoS Attacks.
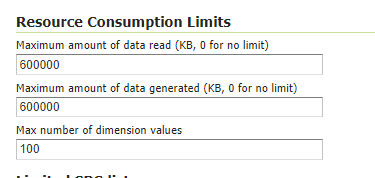
WCS Resource Consuption Limits¶
WMS: Specify here the SRS List you are going to use. Empty means all the ones supported by GeoServer, but be carefull since the
GetCapabilitiesoutput will become huge.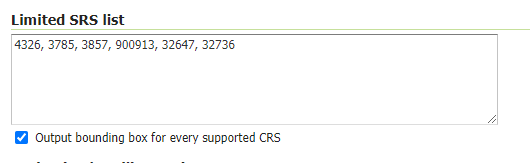
WMS Supported SRS List¶
WMS: Raster Rendering Options allows you to tune up the WMS output for better performance or quality. Best Performance:
Nearest Neighbour- Best Quality:BicubicWarning
Raster Images should be always optimized before ingested into GeoNode. The general recommendation is to never upload a non-processed GeoTIFF image to GeoNode.
Further details at:
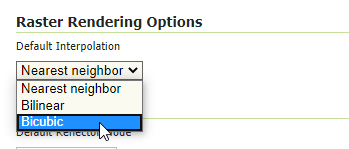
WMS Raster Rendering Options¶
WMS: Update the limits accordingly to your needs. Do not use very high values, this will set GeoServer prone to DoS Attacks.
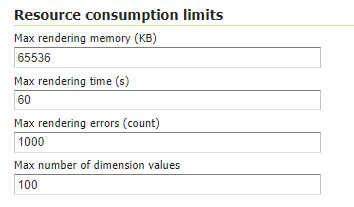
WMS Resource Consuption Limits¶
GeoWebCache DiskQuota On Postgis¶
By default GeoWebCache DiskQuota is disabled. That means that the layers cache might potentially grow up indefinitely.
GeoWebCache DiskQuota should be always enabled on a production system. In the case it is enabled, this must be configured to make use of a DB engine like Postgis to store its indexes.
First of all ensure Tile Caching is enabled on all available layers
Note
GeoNode tipically does this automatically for you. It is worth to double check anyway.
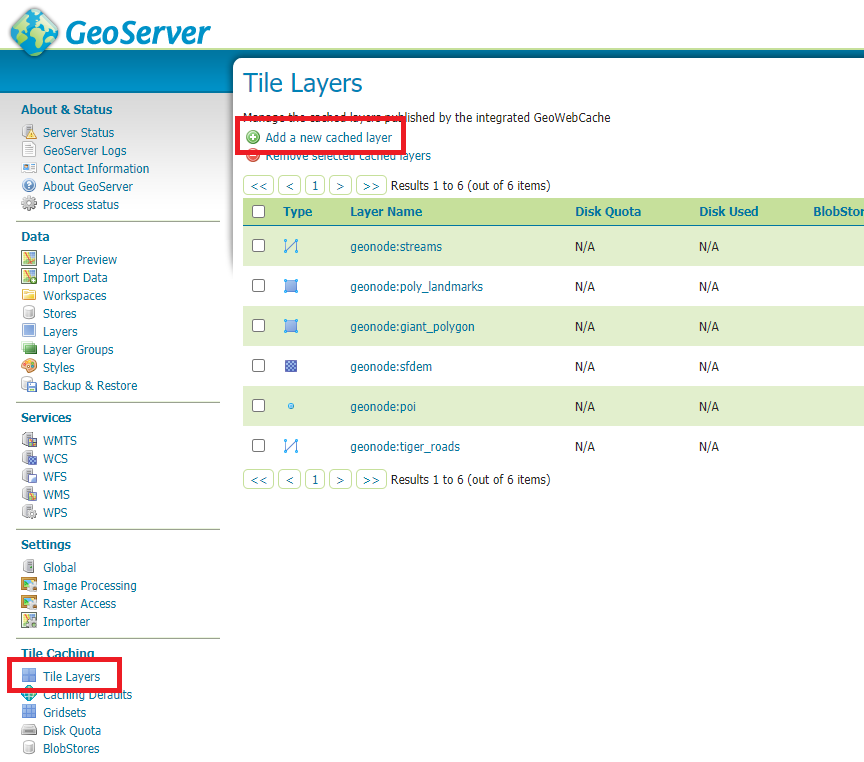
Tile Caching: Tiled Datasets¶
Configure Disk Quota by providing the connection string to the DB Docker Container as specified in the .env file
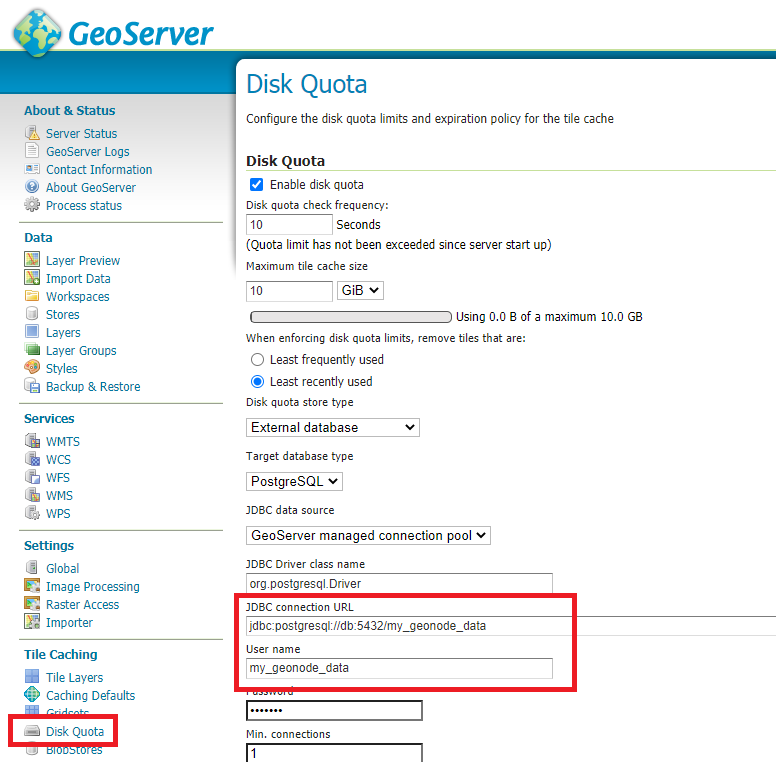
Tile Caching: Disk Quota Configuration¶
GeoFence Security Rules On Postgis¶
By default GeoFence stores the security rules on an H2 db.
On a production system, this is not really recommended. You will need to update the GeoServer Docker container in order to enable GeoFence storing the rules into the DB Docker Container instead.
In order to do that, follow the procedure below:
# Enter the GeoServer Docker Container
docker-compose exec geoserver bash
# Install a suitable editor
apt update
apt install nano
# Edit the GeoFence DataStore .properties file
nano /geoserver_data/data/geofence/geofence-datasource-ovr.properties
Note
Make sure to provide the same connection parameters specified in the .env file
geofenceVendorAdapter.databasePlatform=org.hibernatespatial.postgis.PostgisDialect
geofenceDataSource.driverClassName=org.postgresql.Driver
geofenceDataSource.url=jdbc:postgresql://db:5432/my_geonode_data
geofenceDataSource.username=my_geonode_data
geofenceDataSource.password=********
geofenceEntityManagerFactory.jpaPropertyMap[hibernate.default_schema]=public
# Update the GeoServer WEB-INF/lib JARs accordingly
wget --no-check-certificate "https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/postgis/postgis-jdbc/1.3.3/postgis-jdbc-1.3.3.jar" -O postgis-jdbc-1.3.3.jar && \
wget --no-check-certificate "https://maven.geo-solutions.it/org/hibernatespatial/hibernate-spatial-postgis/1.1.3.2/hibernate-spatial-postgis-1.1.3.2.jar" -O hibernate-spatial-postgis-1.1.3.2.jar && \
rm /usr/local/tomcat/webapps/geoserver/WEB-INF/lib/hibernate-spatial-h2-geodb-1.1.3.1.jar && \
mv hibernate-spatial-postgis-1.1.3.2.jar /usr/local/tomcat/webapps/geoserver/WEB-INF/lib/ && \
mv postgis-jdbc-1.3.3.jar /usr/local/tomcat/webapps/geoserver/WEB-INF/lib/
The container is ready to be restarted now.
Warning
Remember to do a soft restart otherwise the WEB-INF/lib JARs will be reset to the original state
# Exit the GeoServer container
exit
# Soft Restart GeoServer Docker Container
docker-compose restart geoserver
IMPORTANT: The first time you perform this procedure, GeoFence won’t be able to retrieve the old security rules anymore.
You will need to Fixup GeoNode Datasets Permissions in order to regenerate the security rules.
Fixup GeoNode Datasets Permissions¶
The list of the GeoFence Security Rules is available from the GeoFence Data Rules section.
Always double check the list is accessible and the data rules are there. If empty, no layer will be accessible by standard users other than admin.
GeoFence Data Rules¶
In order to re-sync the GeoFence security rules, follow the procedure below:
# Enter the GeoNode Docker Container
docker-compose exec django bash
# Run the `sync_geonode_datasets` management command
./manage.sh sync_geonode_datasets --updatepermissions
Regenerate GeoNode Datasets Thumbnails¶
The following procedure allows you to batch regenerate all Datasets Thumbnails:
# Enter the GeoNode Docker Container
docker-compose exec django bash
# Run the `sync_geonode_datasets` management command
./manage.sh sync_geonode_datasets --updatethumbnails
Regenerate GeoNode Datasets BBOXES¶
The following procedure allows you to batch regenerate all Datasets BBOXES:
# Enter the GeoNode Docker Container
docker-compose exec django bash
# Run the `sync_geonode_datasets` management command
./manage.sh sync_geonode_datasets --updatebbox
Fixup GeoNode Datasets Metadata And Download Links¶
The following procedure allows you to fix-up broken or incorrect Metadata Links:
# Enter the GeoNode Docker Container
docker-compose exec django bash
# Run the `set_all_datasets_metadata` management command
./manage.sh set_all_datasets_metadata -d
It is also possible to force purging the links before regenerating:
# Enter the GeoNode Docker Container
docker-compose exec django bash
# Run the `set_all_datasets_metadata` management command
./manage.sh set_all_datasets_metadata -d --prune
Migrate GeoNode To A New Hostname¶
In the case you will need to move your instance to another domain, as an example from https://my_geonode.geonode.org/ to https://prod_geonode.geonode.org/, follow the procedure below:
Update the .env file by specifyig the new name accordingly.
Restart the GeoNode Docker Container.
docker-compose up -d geonode
Run the following management commands from inside the GeoNode Docker Container.
# Enter the GeoNode Docker Container docker-compose exec django bash # Run the `migrate_baseurl` management command ./manage.sh migrate_baseurl --source-address=my_geonode.geonode.org --target-address=prod_geonode.geonode.org # Run the `set_all_datasets_metadata` management command ./manage.sh set_all_datasets_metadata -d
Add Huge Or DB Datasets To Your Instance¶
Uploaing huge datasets, or DB tables, to GeoNode from the Web Upload Interface is not really possible sometimes.
The suggested procedure in such cases is the following one:
Add the dataset to GeoServer first directly.
You must upload the data into the GeoServer Docker Container Static Volume first and then adding manually the layer throught the GeoServer Admin GUI.
Once the dataset is correctly configured on GeoServer, run the following management command from inside the GeoNode Docker Container
# Enter the GeoNode Docker Container docker-compose exec django bash # Run the `updatelayers` management command ./manage.sh updatelayers -w <workspace_name> -f <layer_name>